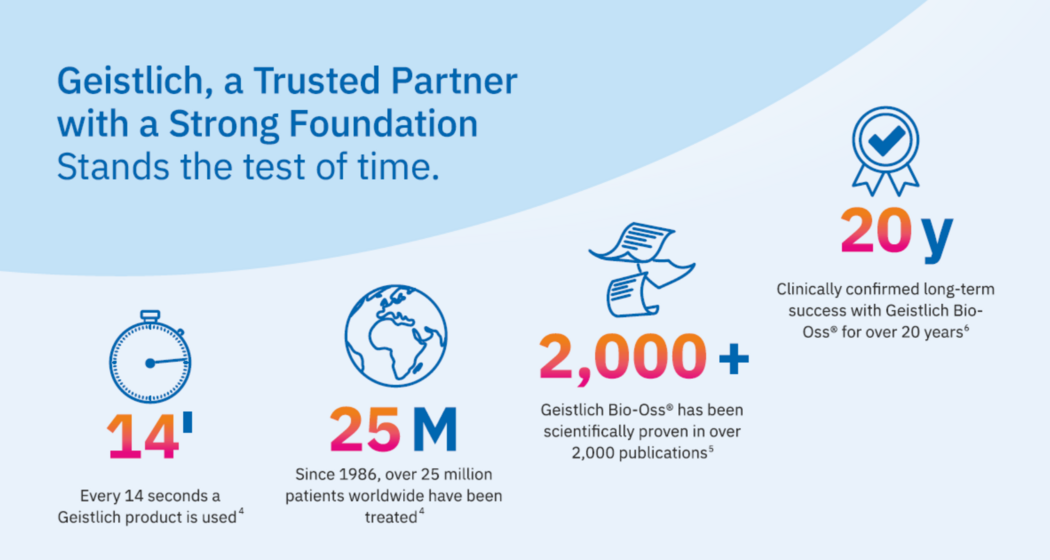
Tooth removal- what next?

When might a dentist suggest removing a tooth?
A dentist may recommend removing a tooth in the following situations:
- Severe decay or damage – When a tooth is deeply decayed, broken, or cannot be repaired.
- Gum disease or loose tooth – When weakened gums can no longer support the tooth.
- Infection or failed treatment – When infection persists despite medicines or repeated dental treatment.
- Space or alignment issues – Tooth removal needed for braces or problematic wisdom teeth.
- Safety or preventive reasons – To prevent spread of cysts, swelling, trauma-related damage, or before major medical treatments.
What are the options, after tooth removal?
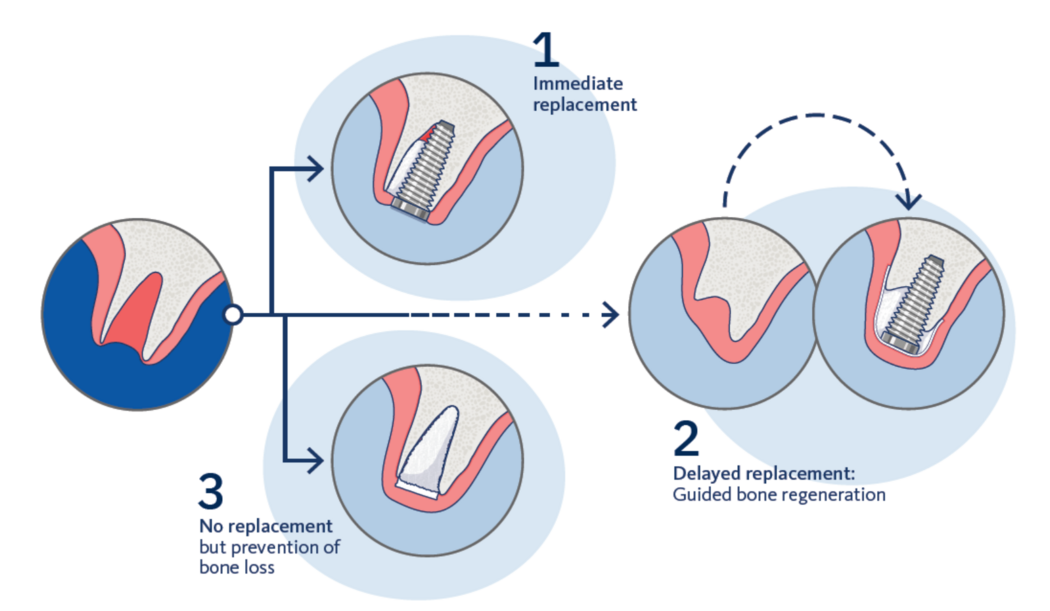
1. Immediate implant placement
In some cases, an implant can be placed right after tooth removal. A bone graft is added around the implant to support it and prevent bone loss. This option may not be suitable for everyone.
2. Delayed implant placement
Sometimes it is preferred to wait and allow the area to heal first. Once healing is complete, an implant is placed. If any bone is missing, bone graft and a protective membrane may be used to rebuild the bone safely.
3. Ridge Preservation
After tooth removal, a bone graft can be placed in the empty space to prevent bone loss. This helps keep the jawbone healthy and gives the patient the option to replace the tooth later with an implant or a dental bridge.
Your dentist will guide you on the best option based on your bone condition and oral health.
What happens after a tooth is removed?
After a tooth is removed, some bone loss naturally happens because the tooth is no longer there to support the jawbone. Over time, the bone in that area may shrink.
This is completely normal. Your dentist can guide you on ways to protect the bone and prepare the area for future tooth replacement options like an implant or dental bridge.
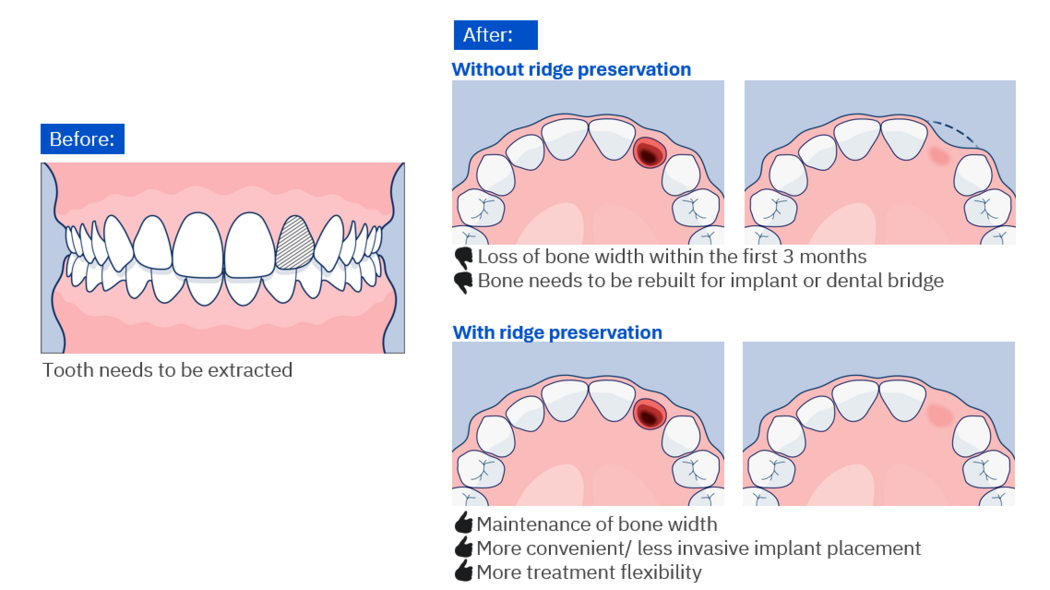
Ridge Preservation With Geistlich Biomaterials: A Predictable Solution